5 Trophic Levels Energy Pyramid
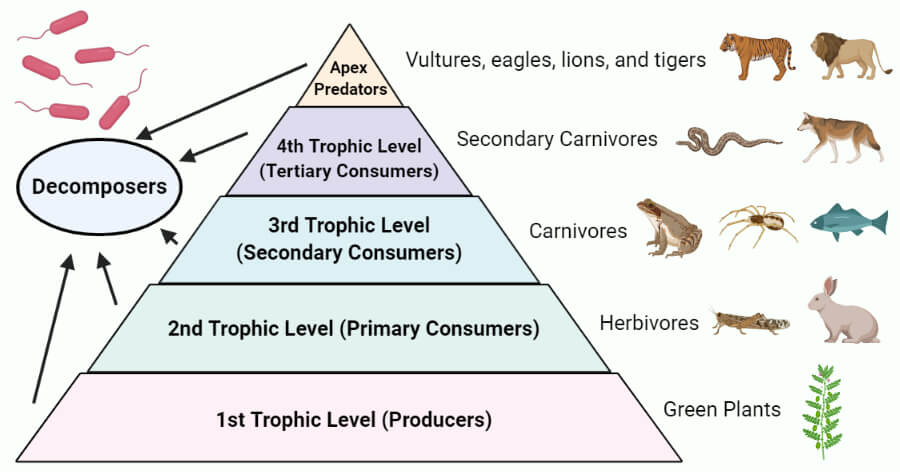
5 Trophic Levels Energy Pyramid The four main trophic levels in an energy pyramid are: 1. producers. producers or autotrophs (grasses, green plants) occupy the first level or at the bottom of the energy pyramid. 2. primary consumers. the second trophic level is occupied by primary consumers or herbivores like grasshoppers that feed on primary producers for food and energy. 3. An energy pyramid (sometimes called a trophic pyramid or an ecological pyramid) is a graphical representation, showing the flow of energy at each trophic level in an ecosystem. the width of each bar represents the units of energy available within each trophic level; the height is always the same. the flow of energy moves through the layers of.

Trophic Pyramid Definition Examples Britannica Trophic pyramid trophic pyramid, also called an energy pyramid, showing the progression of food energy. the pyramid base contains producers, organisms that make their own food from inorganic substances. all other organisms in the pyramid are consumers. the consumers at each level feed on organisms from the level below and are themselves. An ecological pyramid (also trophic pyramid, eltonian pyramid, energy pyramid, or sometimes food pyramid) is a graphical representation designed to show the biomass or bioproductivity at each trophic level in an ecosystem. a pyramid of energy shows how much energy is retained in the form of new biomass from each trophic level, while a pyramid. Draw a terrestrial food chain that includes four trophic levels. identify the trophic level of each organism in the food chain. this page titled 6.5: trophic levels is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. An energy pyramid is useful in quantifying the transfer of energy from one organism to another along a food chain. energy is higher at the bottom of the pyramid, but it decreases as you move up through the trophic levels. namely, as energy flows through the various trophic levels, some energy is normally dissipated as heat at each level.
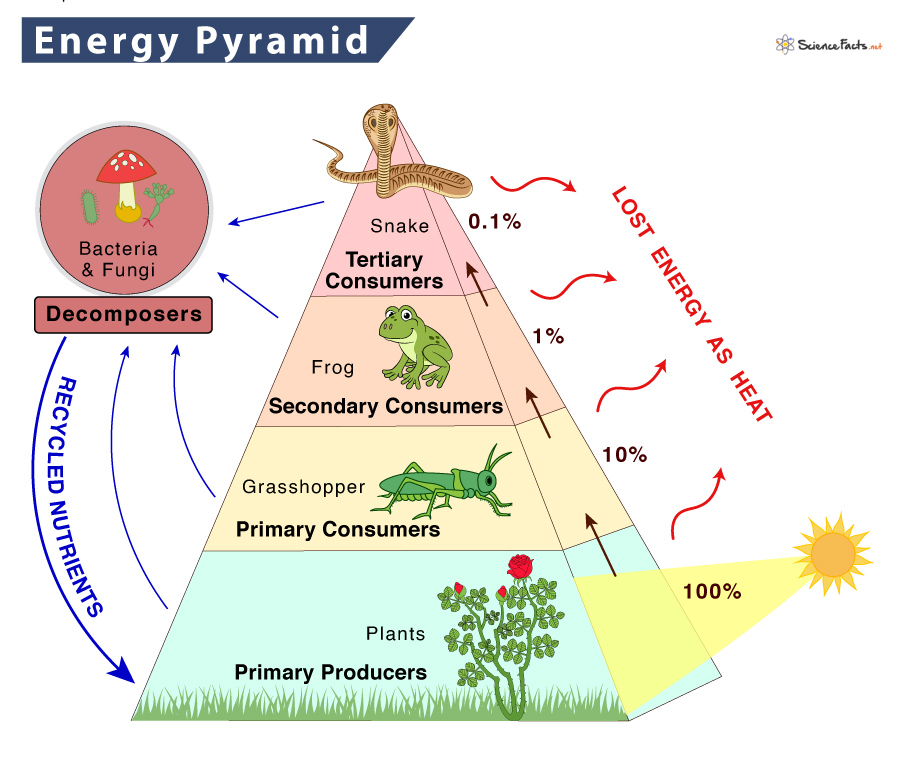
Energy Pyramid вђ Definition Trophic Levels And Example Draw a terrestrial food chain that includes four trophic levels. identify the trophic level of each organism in the food chain. this page titled 6.5: trophic levels is shared under a ck 12 license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by ck 12 foundation via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. An energy pyramid is useful in quantifying the transfer of energy from one organism to another along a food chain. energy is higher at the bottom of the pyramid, but it decreases as you move up through the trophic levels. namely, as energy flows through the various trophic levels, some energy is normally dissipated as heat at each level. A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differs in its nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. Energy transfer and the 10 percent rule. not all food chains and food webs consist of five trophic levels. however, five is the maximum number of trophic levels most ecosystems can support. this is because of inefficiencies in energy flow, which begin with photosynthesis. of all the solar energy that reaches earth, only a small percentage lands.
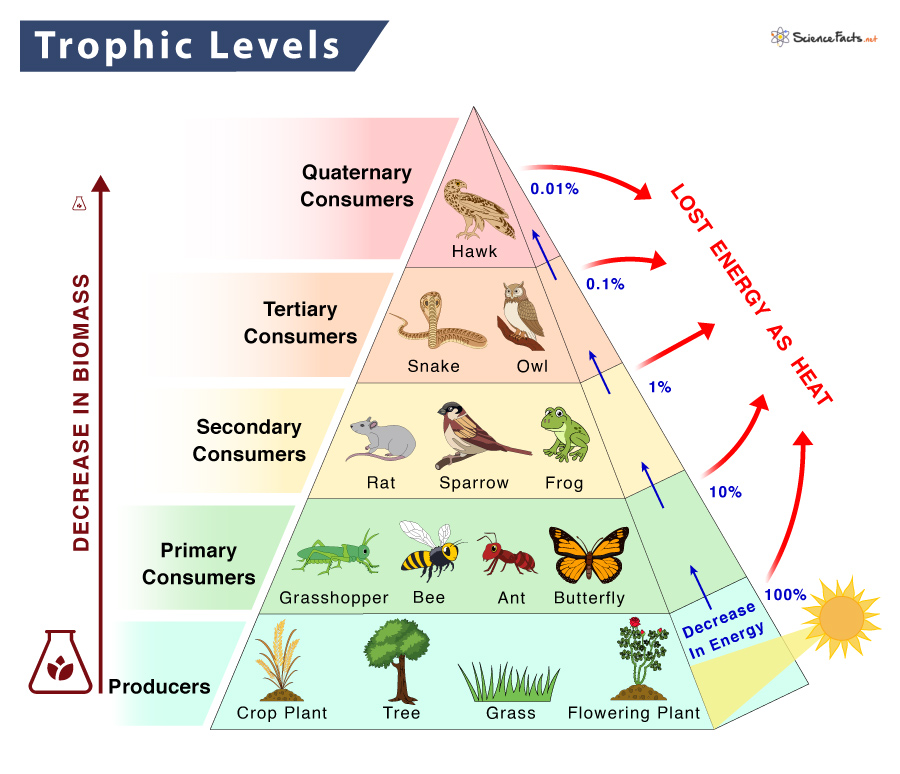
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differs in its nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. Energy transfer and the 10 percent rule. not all food chains and food webs consist of five trophic levels. however, five is the maximum number of trophic levels most ecosystems can support. this is because of inefficiencies in energy flow, which begin with photosynthesis. of all the solar energy that reaches earth, only a small percentage lands.

Comments are closed.