2 Law Of Demand

Law Of Demand Definition Explanation Economics Help In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. in other words, "conditional on all else being equal, as the price of a good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity. The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price, consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. demand is derived from the law of diminishing.
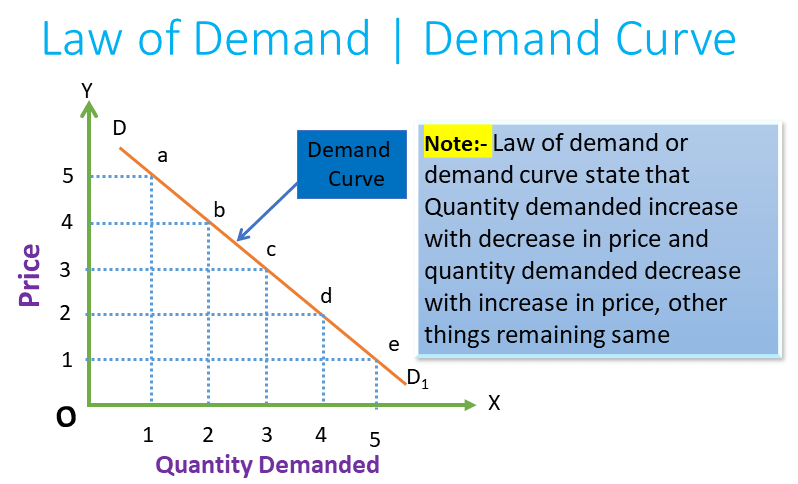
Demand Concept Demand Function Law Of Demand The demand curve is a graph showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded. a demand curve can be for an individual consumer or the whole market (market demand curve) exceptions to the law of demand. giffen good. this is good where a higher price causes an increase in demand (reversing the usual law of demand). The law of demand states that the quantity demanded of a good shows an inverse relationship with the price of a good when other factors are held constant (cetris peribus). it means that as the price increases, demand decreases. the law of demand is a fundamental principle in macroeconomics. it is used together with the law of supply to. Definition. the law of demand states that all other things being equal, the quantity bought of a good or service is a function of price. the law of demand affirms the inverse relationship between price and demand. people will buy less of something when its price rises; they'll buy more when its price falls. the law of demand assumes that all. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
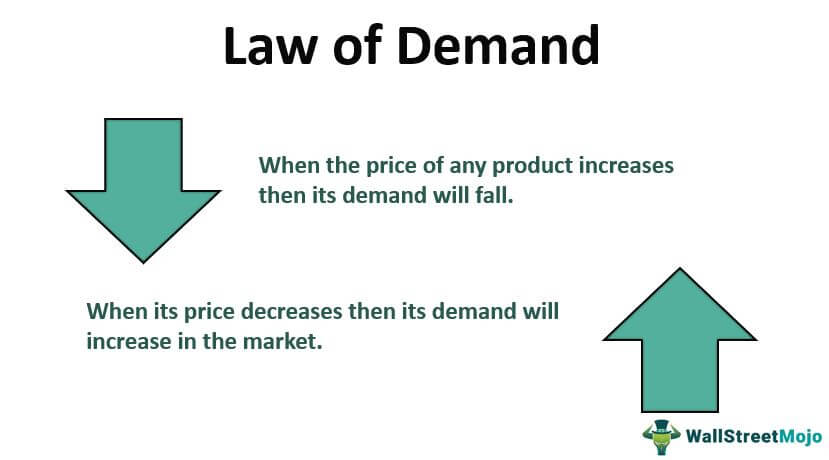
Law Of Demand What Is It Examples Limitations Importance Definition. the law of demand states that all other things being equal, the quantity bought of a good or service is a function of price. the law of demand affirms the inverse relationship between price and demand. people will buy less of something when its price rises; they'll buy more when its price falls. the law of demand assumes that all. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Law of demand: definition and examples. written by masterclass. last updated: aug 31, 2022 • 2 min read. the law of demand is one of the most basic economic theories. learn how it works, and how it’s different from—but related to—the law of supply. explore. The law of demand is the basic law in economics that serves as the foundation of market analysis. it describes the inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded, where an increase in the price of a good or service leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded, and vice versa. if there is a rise in the price of a good, its.

Law Of Demand Explained With Example Tutor S Tips Law of demand: definition and examples. written by masterclass. last updated: aug 31, 2022 • 2 min read. the law of demand is one of the most basic economic theories. learn how it works, and how it’s different from—but related to—the law of supply. explore. The law of demand is the basic law in economics that serves as the foundation of market analysis. it describes the inverse relationship between the price and the quantity demanded, where an increase in the price of a good or service leads to a decrease in the quantity demanded, and vice versa. if there is a rise in the price of a good, its.

Comments are closed.