10 Differences Between Bacteria And Fungi Bacteria Vs Vrogue Co
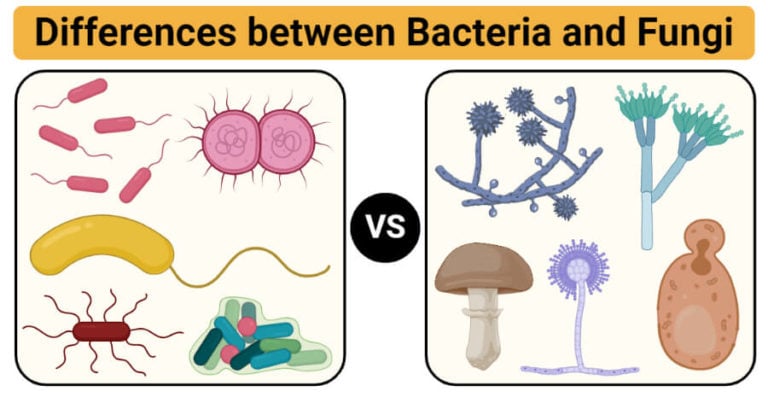
Bacteria Vs Fungi Definition 21 Major Differences Examples Bacteria and fungi come under different categories; the former one is the prokaryotic cell while the latter one is eukaryotic cells.apart from this, there are many differences between them like bacteria need a host to live, and they can be autotrophs as well as heterotrophs, whereas fungi grow their own and are heterotrophs which depend on others for their food. Fungi generally are the decomposers of the ecosystem. most bacteria grow best around neutral ph values (6.5 7.0) most fungi grow best around slightly acidic ph (4 6) bacteria are unicellular organisms that are visible only under microscope. fungi are unicellular (yeast) or multi cellular filamentous organisms with hyphae and mycelium.
10 Differences Between Bacteria And Fungi Bacteria Vs Vrogue Co Bacteria grow best in the neutral environment of ph range 6.5 7. fungi mostly prefer a slightly acidic environment with ph value 4 6. mobility. some bacteria are motile with flagella. fungi are immobile organisms. nucleus. the genetic material in bacteria is localized in the nuclear region of the cytoplasm. The main difference between bacteria and fungi is that bacteria are unicellular prokaryotic organisms whereas fungi are multicellular eukaryotic organisms. both bacteria and fungi contain dna as their genetic material. the genetic material of bacteria is organized in the cytoplasm. but in fungi, it is organized inside the nucleus. Bacteria have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles. they power the food cycle, nitrogen fixation, and breakdown despite their modest size. symbiotic bacteria help plants and animals survive and flourish. eukaryotic fungi include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. fungi have nuclei and membrane bound organelles, unlike bacteria. Fungi contain microtubules as well as microfilaments. bacteria have cell cycles that are shorter between 20 and 60 minutes. fungi have longer cycles of cell cycle that range between 12 and 24 hours. tuberculosis, tetanus and leprosy as well as typhoid and as well as cholera, are caused by bacteria.

10 Differences Between Bacteria And Fungi Bacteria Vs Vrogue Co Bacteria have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles. they power the food cycle, nitrogen fixation, and breakdown despite their modest size. symbiotic bacteria help plants and animals survive and flourish. eukaryotic fungi include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. fungi have nuclei and membrane bound organelles, unlike bacteria. Fungi contain microtubules as well as microfilaments. bacteria have cell cycles that are shorter between 20 and 60 minutes. fungi have longer cycles of cell cycle that range between 12 and 24 hours. tuberculosis, tetanus and leprosy as well as typhoid and as well as cholera, are caused by bacteria. Fungi belong to the kingdom mycota. hyphae (mold) and yeast are the common morphological forms. bacteria are smaller in comparison to fungi (average size: about 1 5 microns). the fungi are larger than bacteria (average size: about 5 50 micrometers). bacteria reproduce asexually (binary fission). On the other hand, fungi are eukaryotic organisms with complex cellular structures. they have a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, and a cell wall composed of chitin. fungi are typically multicellular, although some species exist as single celled yeasts. reproduction. bacteria reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission.
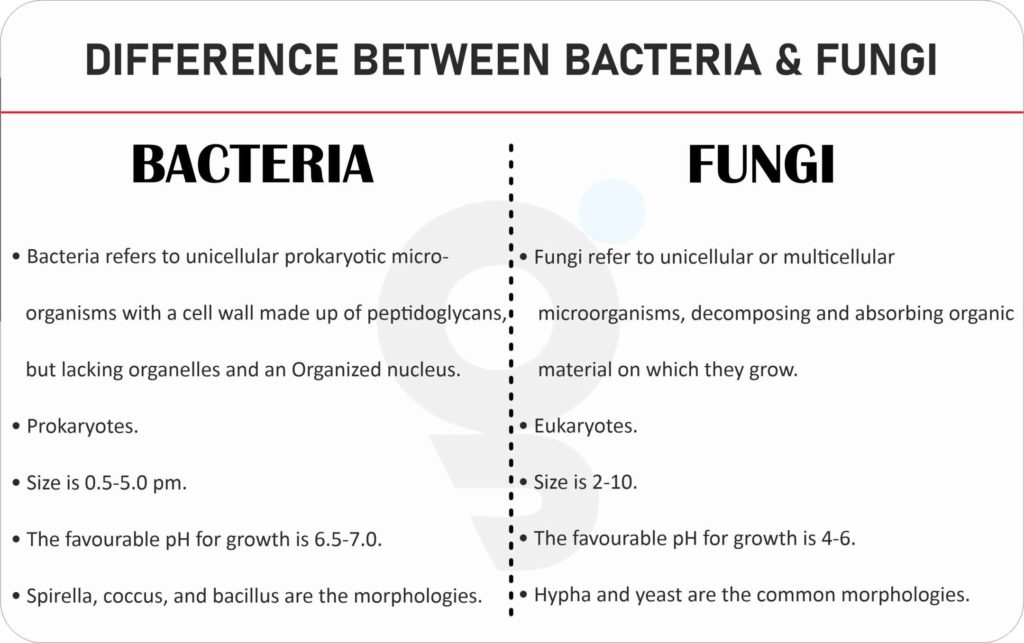
Difference Between Bacteria Viruses And Fungi Naturew Vrogue Co Fungi belong to the kingdom mycota. hyphae (mold) and yeast are the common morphological forms. bacteria are smaller in comparison to fungi (average size: about 1 5 microns). the fungi are larger than bacteria (average size: about 5 50 micrometers). bacteria reproduce asexually (binary fission). On the other hand, fungi are eukaryotic organisms with complex cellular structures. they have a nucleus, membrane bound organelles, and a cell wall composed of chitin. fungi are typically multicellular, although some species exist as single celled yeasts. reproduction. bacteria reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission.
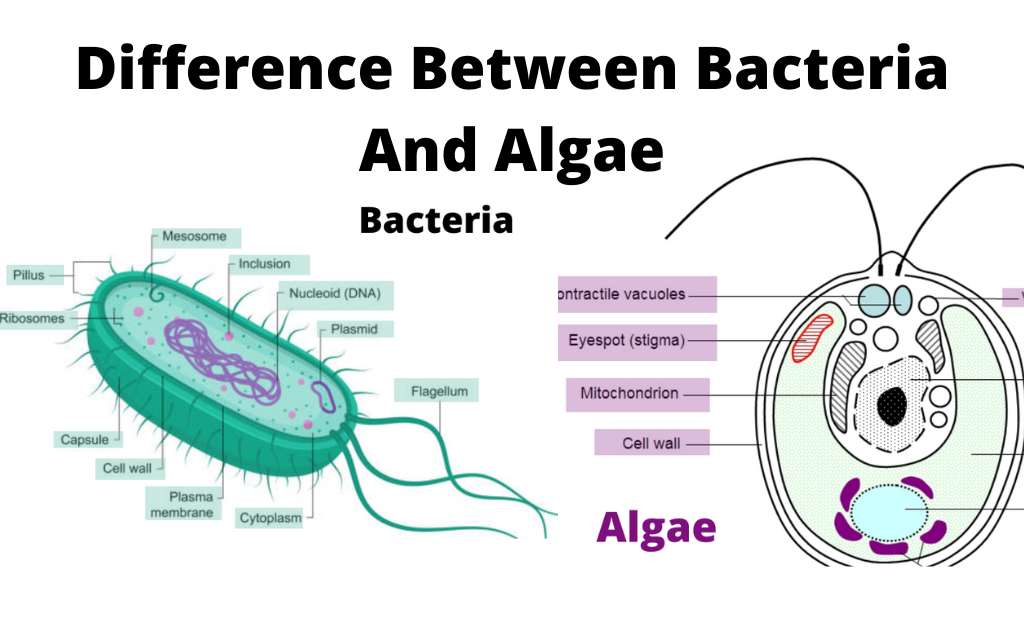
10 Differences Between Bacteria And Fungi Bacteria Vs Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.